Difference between revisions of "Aegean"
(New page: Aegean Diplomacy Image:Aegean_RP.gif Image:Aegean10 Names.gif Variant Rules: 1) Except as noted below, the standard rules of play for Diplomacy on the judge apply. 2) This ...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Image:Aegean_RP.gif]] | [[Image:Aegean_RP.gif]] | ||
| Line 8: | Line 5: | ||
Variant Rules: | Variant Rules: | ||
| + | 1) Except as noted below, the standard rules of play for Diplomacy apply. | ||
| − | + | 2) This game is played on a map representing the Aegean Sea during the Vth | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | 2) This game is played on a map representing | ||
and IVth centuries BC. | and IVth centuries BC. | ||
| − | + | 3) Game starts in Spring 475 BC, soon after the Medic Wars. The game is calculated in years after the first Olympic games in 776 BC, so the game starts | |
| − | 3) Game starts in Spring 475 BC, soon after the Medic Wars. | ||
| − | |||
| − | years after the first Olympic games in 776 BC, so the game starts | ||
in S301M. | in S301M. | ||
| − | + | 4) There are 38 supply centers. The victory condition is possession of | |
| − | 4) There are 38 supply centers. | ||
20 centers at the end of any Fall retreat. | 20 centers at the end of any Fall retreat. | ||
| − | + | 5) There are seven great powers. The starting units are as follows: | |
| − | 5) There are seven great powers. | ||
| − | |||
| − | The starting units are as follows: | ||
| − | |||
A-ATHENS | A-ATHENS | ||
| − | + | *A Athens | |
| − | + | *F Aegina | |
| − | + | *F Delos | |
| − | |||
B-BOEOTIA | B-BOEOTIA | ||
| − | + | *A Thebes | |
| − | + | *A Delphi | |
| − | + | *F Naupactus | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
I-IONIA | I-IONIA | ||
| − | + | *F Miletus | |
| − | + | *F Chios | |
| − | + | *F Samos | |
| + | M-MACEDONIA | ||
| + | *A Pella | ||
| + | *A Therma | ||
| + | *F Amphipolis | ||
P-PERSIA | P-PERSIA | ||
| − | + | *A Sardes | |
| − | + | *F Cyzicus | |
| − | + | *A Pergamum | |
| − | + | *F Halicarnassus | |
| − | |||
S-SPARTA | S-SPARTA | ||
| − | + | *A Sparta | |
| − | + | *F Pylos | |
| − | + | *A Zarax | |
| − | |||
T-THESSALIA | T-THESSALIA | ||
| − | + | *A Pharsalus | |
| − | + | *A Larissa | |
| − | + | *F Pherae | |
| − | |||
6) A player may build on any supply center he owns which is vacant as | 6) A player may build on any supply center he owns which is vacant as | ||
| − | long as he still owns at least one of his original centers (Aberration | + | long as he still owns at least one of his original centers ([[Aberration |
| − | + | Builds]]). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | 7) All the coastal provinces have one unique coast. | ||
8) 12 bridges connect some islands with continent, or close coastal | 8) 12 bridges connect some islands with continent, or close coastal | ||
| Line 90: | Line 64: | ||
effect any fleet moving in the see spaces crossed by the bridge. | effect any fleet moving in the see spaces crossed by the bridge. | ||
| − | + | These bridges connect the following provinces: | |
| − | These bridges connect the following provinces : | + | *byz - phr |
| − | + | *thr - cyz | |
| − | + | *thr - tro | |
| − | + | *the - cha | |
| − | + | *sam - mil | |
| − | + | *pht - cha | |
| − | + | *dia - eub | |
| − | + | *ath - eub | |
| − | + | *nau - ach | |
| − | + | *act - aeg | |
| − | + | *ath - aeg | |
| − | + | *meg - aeg | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
9) The unnamed spaces as Corcyra for example are not usable for units. | 9) The unnamed spaces as Corcyra for example are not usable for units. | ||
| − | + | 10) Six supply centers are islands surrounded by sea, so they are | |
| − | 10) Six supply centers are islands surrounded by | ||
both land and see territories. Fleets can move normally to these islands, | both land and see territories. Fleets can move normally to these islands, | ||
and a fleet which is in an island can make a convoy. To move to an island, | and a fleet which is in an island can make a convoy. To move to an island, | ||
| Line 116: | Line 87: | ||
can move to Ithaca normally. These island centers are Ithaca, Aegina, | can move to Ithaca normally. These island centers are Ithaca, Aegina, | ||
Delos, Lesbos, Chios and Samos. | Delos, Lesbos, Chios and Samos. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Map Abbreviations: | Map Abbreviations: | ||
| − | |||
One-word territory names are abbreviated by their first three letters, | One-word territory names are abbreviated by their first three letters, | ||
except the following: | except the following: | ||
| − | + | Olynthus olt | |
| − | Olynthus olt | + | Therma thm |
| − | Therma thm | + | Delos dls |
| − | Delos dls | ||
| − | |||
Two-words territory names are abbreviated by the first two letters of | Two-words territory names are abbreviated by the first two letters of | ||
the first word, and the initial of the second, except the following: | the first word, and the initial of the second, except the following: | ||
| − | + | Pontus Euxinus pon North Sporades nsp | |
| − | Pontus Euxinus pon North Sporades nsp | + | South Sporades ssp West Cyclades wcy |
| − | South Sporades ssp West Cyclades wcy | + | East Cyclades ecy |
| − | East Cyclades ecy | ||
| − | |||
Three-words territory names are abbreviated by the three initials. | Three-words territory names are abbreviated by the three initials. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Historical Background: | Historical Background: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
499 BC : The cities of the Ionian League, which had developped a brillant | 499 BC : The cities of the Ionian League, which had developped a brillant | ||
| Line 153: | Line 113: | ||
king of Persia, squelches the revolt and attempts to dominate the Greek | king of Persia, squelches the revolt and attempts to dominate the Greek | ||
cities on the continent. | cities on the continent. | ||
| − | |||
490 BC : First Medic war. Athens defeats the Persian army in Marathon, near | 490 BC : First Medic war. Athens defeats the Persian army in Marathon, near | ||
Athens. Xerxes, son of Darius, prepares for a great expedition while the | Athens. Xerxes, son of Darius, prepares for a great expedition while the | ||
Greeks attempt to unite under Spartan rule. | Greeks attempt to unite under Spartan rule. | ||
| − | |||
480 BC : Second Medic war. Xerxes subjects Northern Greece, crushes Leonidas's | 480 BC : Second Medic war. Xerxes subjects Northern Greece, crushes Leonidas's | ||
| Line 165: | Line 123: | ||
commander of the Athenian fleet. The next year, the Spartan army (led by | commander of the Athenian fleet. The next year, the Spartan army (led by | ||
Pausanias) defeats the Persian troops in Plataea, Boeotia. Greece is freed | Pausanias) defeats the Persian troops in Plataea, Boeotia. Greece is freed | ||
| − | from | + | from the Persian yoke. |
| − | the Persian yoke. | ||
| − | |||
479-431 : The Golden Years of Athens: most of the cities of the Aegean coasts | 479-431 : The Golden Years of Athens: most of the cities of the Aegean coasts | ||
| Line 174: | Line 130: | ||
"Peloponnesian League" under Spartan rule. Numerous conflicts exist between | "Peloponnesian League" under Spartan rule. Numerous conflicts exist between | ||
these two alliances. | these two alliances. | ||
| − | |||
431-404 : The Peloponnesian war sets the Spartan League (which is also allied | 431-404 : The Peloponnesian war sets the Spartan League (which is also allied | ||
| Line 181: | Line 136: | ||
fleet, the walls of Athens are razed to the ground and the Delos league is | fleet, the walls of Athens are razed to the ground and the Delos league is | ||
broken up. | broken up. | ||
| − | |||
The IVth century : The turn of the century is marked by the Spartan hegemony, | The IVth century : The turn of the century is marked by the Spartan hegemony, | ||
| Line 190: | Line 144: | ||
Epaminondas is killed in the battle of Mantinea (Arcadia) against the | Epaminondas is killed in the battle of Mantinea (Arcadia) against the | ||
Athens-Sparta coalition in 362. | Athens-Sparta coalition in 362. | ||
| − | |||
After Mantinea, the three hegemonic cities start to weaken while, in the | After Mantinea, the three hegemonic cities start to weaken while, in the | ||
| − | North, | + | North, the powerful kingdom of Macedonia is forming. Philippe II (356-336) unifies his territory, raises a powerful army and becomes the leader of the Thessalian league around 344. He becomes more and more involved in Greek affairs. In 338, in Coronea (Boeotia), he defeats the Thebans, Athenians and their allies and imposes peace as the leader of the whole Greece. |
| − | the powerful kingdom of Macedonia is forming. Philippe II (356-336) unifies | ||
| − | his territory, raises a powerful army and becomes the leader of the Thessalian | ||
| − | league around 344. He becomes more and more involved in Greek affairs. In 338, | ||
| − | in Coronea (Boeotia), he defeats the Thebans, Athenians and their allies and | ||
| − | imposes peace as the leader of the whole Greece. | ||
| − | |||
His son, Alexander the Great (336-324) can now set out to conquer the Persian | His son, Alexander the Great (336-324) can now set out to conquer the Persian | ||
Empire... | Empire... | ||
Revision as of 21:09, 21 April 2008
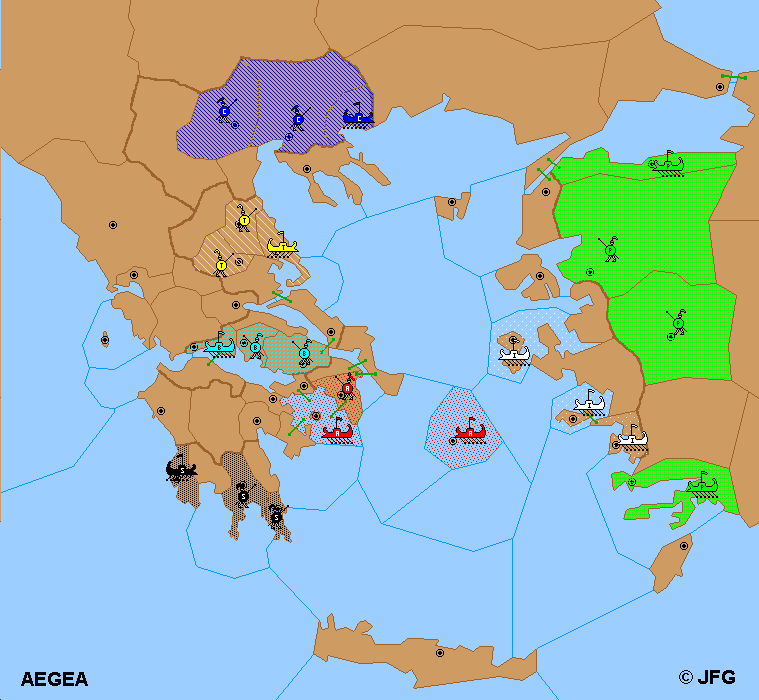
Variant Rules:
1) Except as noted below, the standard rules of play for Diplomacy apply.
2) This game is played on a map representing the Aegean Sea during the Vth and IVth centuries BC.
3) Game starts in Spring 475 BC, soon after the Medic Wars. The game is calculated in years after the first Olympic games in 776 BC, so the game starts in S301M.
4) There are 38 supply centers. The victory condition is possession of 20 centers at the end of any Fall retreat.
5) There are seven great powers. The starting units are as follows:
A-ATHENS
- A Athens
- F Aegina
- F Delos
B-BOEOTIA
- A Thebes
- A Delphi
- F Naupactus
I-IONIA
- F Miletus
- F Chios
- F Samos
M-MACEDONIA
- A Pella
- A Therma
- F Amphipolis
P-PERSIA
- A Sardes
- F Cyzicus
- A Pergamum
- F Halicarnassus
S-SPARTA
- A Sparta
- F Pylos
- A Zarax
T-THESSALIA
- A Pharsalus
- A Larissa
- F Pherae
6) A player may build on any supply center he owns which is vacant as long as he still owns at least one of his original centers ([[Aberration Builds]]).
7) All the coastal provinces have one unique coast.
8) 12 bridges connect some islands with continent, or close coastal territories. A moving unit (fleet or army) using a bridge doesn't effect any fleet moving in the see spaces crossed by the bridge.
These bridges connect the following provinces:
- byz - phr
- thr - cyz
- thr - tro
- the - cha
- sam - mil
- pht - cha
- dia - eub
- ath - eub
- nau - ach
- act - aeg
- ath - aeg
- meg - aeg
9) The unnamed spaces as Corcyra for example are not usable for units.
10) Six supply centers are islands surrounded by sea, so they are both land and see territories. Fleets can move normally to these islands, and a fleet which is in an island can make a convoy. To move to an island, an army must be convoyed, or use a bridge. Ithaca is an exception: because this center includes continental territory, an army in Ambracia or Aetolia can move to Ithaca normally. These island centers are Ithaca, Aegina, Delos, Lesbos, Chios and Samos.
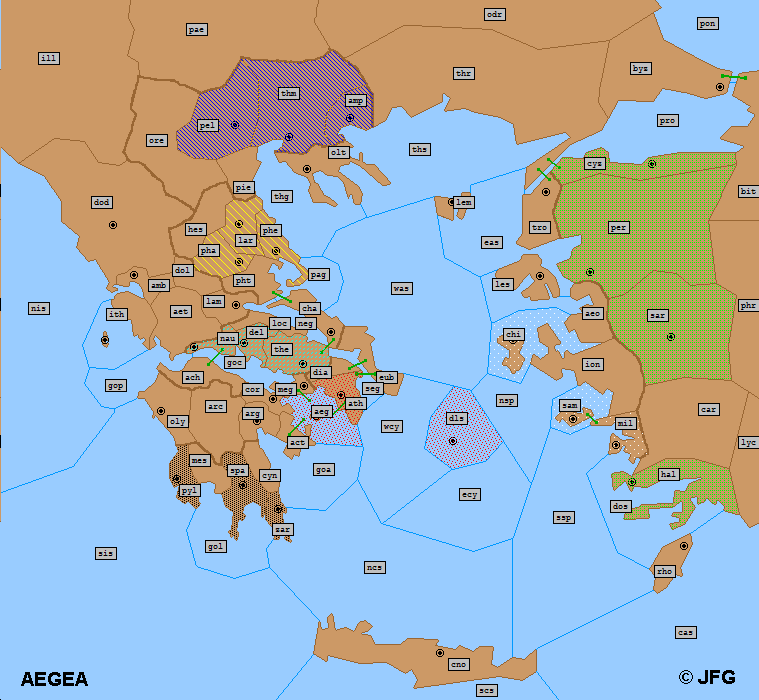
Map Abbreviations:
One-word territory names are abbreviated by their first three letters, except the following:
Olynthus olt Therma thm Delos dls
Two-words territory names are abbreviated by the first two letters of the first word, and the initial of the second, except the following:
Pontus Euxinus pon North Sporades nsp South Sporades ssp West Cyclades wcy East Cyclades ecy
Three-words territory names are abbreviated by the three initials.
Historical Background:
499 BC : The cities of the Ionian League, which had developped a brillant civilization in the course of the earlier centuries, rebel against the Persian rule under the command of tyrant Aristagoras of Miletus. Darius, king of Persia, squelches the revolt and attempts to dominate the Greek cities on the continent.
490 BC : First Medic war. Athens defeats the Persian army in Marathon, near Athens. Xerxes, son of Darius, prepares for a great expedition while the Greeks attempt to unite under Spartan rule.
480 BC : Second Medic war. Xerxes subjects Northern Greece, crushes Leonidas's heroïc Spartan army in Thermopylae (East Locris). Athens is destroyed by fire. But the Persian fleet is vanquished in Salamis (Aegina Gulf) by Themistocles, commander of the Athenian fleet. The next year, the Spartan army (led by Pausanias) defeats the Persian troops in Plataea, Boeotia. Greece is freed from the Persian yoke.
479-431 : The Golden Years of Athens: most of the cities of the Aegean coasts are brought together in a "Delos League" which soon develops so as to form the Empire of Athens. Meantime, most of the Southern cities are federated in the "Peloponnesian League" under Spartan rule. Numerous conflicts exist between these two alliances.
431-404 : The Peloponnesian war sets the Spartan League (which is also allied to Thebes) against the Empire of Athens, led by Pericles and later on by Alcibiade. Lysandre, naval commander of Lacedemonians, destroys the Athenian fleet, the walls of Athens are razed to the ground and the Delos league is broken up.
The IVth century : The turn of the century is marked by the Spartan hegemony, led by king Agesilas, but it is soon disputed by Athens (which forms another confederation) and Thebes, which brings together the Boeotian League, while Jason of Pherae unifies Thessaly under his rule. In 371, Epaminondas, the leader of the Theban army, beats the Spartans in Leuctra, in Boeotia, but Epaminondas is killed in the battle of Mantinea (Arcadia) against the Athens-Sparta coalition in 362.
After Mantinea, the three hegemonic cities start to weaken while, in the North, the powerful kingdom of Macedonia is forming. Philippe II (356-336) unifies his territory, raises a powerful army and becomes the leader of the Thessalian league around 344. He becomes more and more involved in Greek affairs. In 338, in Coronea (Boeotia), he defeats the Thebans, Athenians and their allies and imposes peace as the leader of the whole Greece.
His son, Alexander the Great (336-324) can now set out to conquer the Persian Empire...